
Created with GIMP
Switching to lightweight construction is proving to be a challenge for most automotive manufacturers.
It is usually associated with higher costs, thanks to more costly materials and to the greater complexity of the design. German firm Bionic Mesh Design believes it can help reduce the costs.
The company says it is providing CAD designs which respect the constraints of the desired manufacturing method while fully maintaining the complex organic shapes coming from topology optimizations to achieve maximum lightweighting.
“We are a team of experienced engineers from the fields of automotive, motorsport and aerospace with simulation, optimization and cad background. Our focus is on making lightweight construction affordable and accessible for everyone.
“We have made it our mission to save your money with lightweight design. We develop the lightest possible components in the manufacturing process you require in an unbeatable time,” says the company.
Its customers include major original equipment manufacturers (OEMs) and Tier 1s such as BMW, GKN, Pankl, MV Augusta, and Zeiss.

“It is widely acknowledged that relying on topology optimization can lead to lightweight components. Until now a consistent application of structural optimization has been restricted due to the complexity of the topology results and the costly and time-consuming process to realize these results in CAD.
“In order to keep the full lightweight potential of topology optimization outputs it is mandatory to generate CAD components which are fully based on them,” says Bionic Mesh in a statement.
Bionic Mesh won the runner up prize in the enabling technology category at the Altair Enlighten Award 2022.
The award, given in association with the Center for Automotive Research (CAR), is given for breakthroughs in sustainability and light-weighting advancements that successfully reduce carbon footprint, mitigate water and energy consumption, and leverage material reuse and recycling efforts.
“Bionic Mesh Design has refined and redefined lightweight design for mass casting and forging productions.
“These lightweight designs are achieved through the direct transformation of topology in CAD models and an emphasis on production processes. By requiring 90% less design time than standard solid modelling processes, Bionic Mesh Design helps automotive OEMs and suppliers get products to market faster,” said a press release from Altair.
“The caliber of nominees for this year’s Enlighten Award was unparalleled and is a true testament to the investments the automotive industry is making to reach – and even exceed – global sustainability targets,” said Richard Yen, senior vice president, product and strategy, Altair in an August 2022 media release.
“As we celebrate our tenth year and have evaluated hundreds of worthy entries over the years, we have seen this award evolve from showcasing vehicle light-weighting initiatives to companies now fully embracing sustainability and the commitment to building a net-zero environment and circular economy.”
“The winners of the 2022 Enlighten Award have demonstrated the great strides the automotive industry has made in creating more sustainable products,” said Carla Bailo, president and CEO, Center for Automotive Research in the same media statement. “Collaborating with Altair over the past ten years has allowed us to showcase on a global stage the automotive sector’s most unique and proven approaches to meet weight reduction and sustainability goals.”
Automotive Industries (AI) asked Thomas Spoida, Founder and CEO, Bionic Mesh Design, to tell us how the company’s technology reduces the cost of lightweighting.

Spoida: We take as much mass out of the components as possible. Using less material leads to cheaper components. Depending on the volume this can mean savings of several million Euros/Dollars for the OEM for each component.
The key to achieve that is to fully rely on topology optimizations to define the ideal shape for each component.
AI: Topology optimization is not a new concept
Spoida: That is true. It has been around for decades and has been integrated in many commercial software tools. To use these tools properly you have to be a simulation expert, and it also requires a deep knowledge of the desired manufacturing method to define the right input for the optimization.
To date, the biggest problem is to generate clean manufacturable CAD based on the topology results. It would take weeks to create a design that respects all the “bionic“ features from the optimization result by using standard solid modeling in CAD.
As design cycles in the automotive industry are getting faster and faster there is simply now time for that and you have simplify the complex optimized shapes which is reducing the mass saving potential of the topology optimization.
AI: What is your solution?
Spoida: In addition to the CAD world, there is another area that deals with three-dimensional digital content. Everything you see in a computer game, or an animated movie, is modeled in three dimensions and is often much more complex than mechanical components.
The tools used for this have to enable the user to create large numbers of highly complex shapes in the shortest possible time as this market is growing continuously.
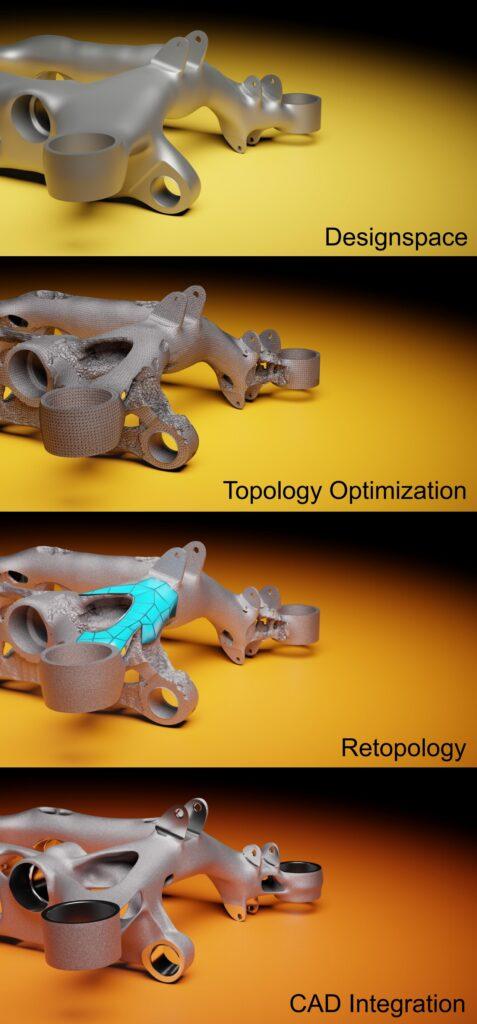
Thanks to existing interfaces. we are able to use tools such as ZBrush and Cinema4D to generate manufacturable CAD data for all manufacturing processes based on topology optimization results.
The technology these programs use is already implemented in all major CAD tools, which allows us to export our data to e.g. Catia or Siemens NX and even further adapt it there as a living so-called subdivision body. This is very important as our customers would not normally accept “dead” step or iges files.
AI: Why is subdivision modeling used so rarely by engineers?
Spoida: It is mainly advertised as a styling tool to quickly generate some nice-looking handles, for example, and not for structural components. Another problem is that there are no subdivision modeling features in CAD available that allow for a quick remodeling of topology results. And the CAD integrated solutions do not perform as well as we need them to be.
AI: What does your service mean for your customers?
Spoida: Our workflow has two main benefits: Our customers ca
n be sure to get the lightest possible design for their desired production method. And we can provide this very quickly.
It has been shown that we can reduce design time by 50 to 90% by using these artist tools, compared to legacy CAD systems.
Usually we have to respond to many package changes during our development projects. With subdivision modelling design, modifications can be done in real time and trials of different manufacturing methods can be carried out with final CAD models.
Another great benefit of subdivision is that we can generate simulation models directly without the need for CAD modeling and subsequent CAE meshing. This saves a significant amount of development time.
AI: Why is it critical to develop technologies that bring down the cost of lightweighting?
Spoida: I believe that lightweighting with an environmental impact can only happen on large volume production methods.
Lightweight manufacturing methods like composites and 3D-printing are great innovations and contribute their part to weight reduction, but only to a very limited extent to date.
We are mainly focusing on casting and forging. Looking at trends such as giga castings, this is where the greatest potential for lightweight construction in vehicle construction lies in the medium term.
We must also not forget the positive side effect of lighter components on the mass of crash absorbing structures. Less mass means less kinetic energy to be absorbed during a crash event.











More Stories
DuPont materials science advances next generation of EV batteries at The Battery Show
Your Guide to Filing a Car Accident Claim
Steps to Take Immediately After a Car Accident