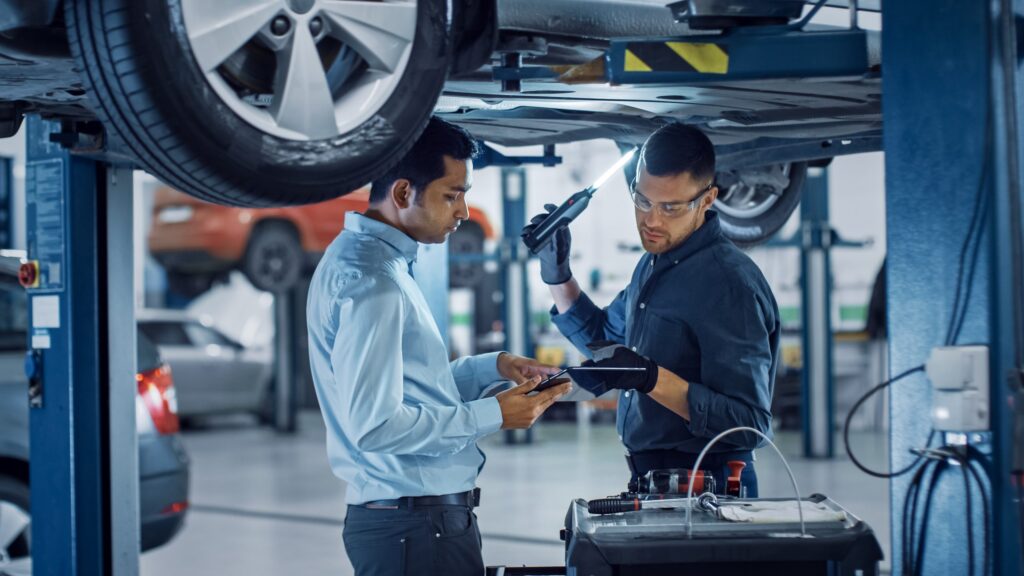

In the era of connected vehicles and advanced automotive technologies, cybersecurity has become a critical concern for manufacturers and the general public. As the automotive industry continues to embrace innovations such as the introduction of remote updates and sophisticated auto software systems, the need for robust cybersecurity measures becomes paramount.
Let’s unpack the cybersecurity vulnerabilities specific to automotive software and explore effective detection and response strategies, all while keeping a very watchful eye on the unique challenges impacting the industry.
Why is Cybersecurity Critical for Automotive Software?
Integrating digital technologies and software-driven components in modern vehicles has significantly enhanced performance, efficiency, and user experience. However, this digital evolution has also exposed automobiles to potential cyber threats that didn’t exist before. Unlike traditional mechanical issues, cybersecurity threats can compromise not only the functionality of a vehicle but also the safety of its occupants and that of others on the road. With electric vehicles becoming increasingly prevalent, the focus on securing critical components, such as EV batteries, becomes paramount to prevent unauthorized access or malicious attacks.
Top Automotive Cybersecurity Vulnerabilities
Automotive cybersecurity vulnerabilities pose a significant risk to the integrity and safety of vehicles. Addressing these vulnerabilities is paramount, as it ensures the protection of in-car systems from potential exploits, unauthorized access, and malicious manipulations, safeguarding both user safety and the overall functionality of automotive software.
Remote Exploitation
With the rise of connected vehicles, the risk of remote exploitation has increased drastically. Hackers may attempt to compromise vehicle software through wireless connections, gaining unauthorized access to control systems.
Inadequate Authentication
Weak authentication mechanisms can open doors for unauthorized users to manipulate software functionalities. This is particularly concerning when considering the sensitive nature of the electric vehicle battery and its crucial role in vehicle operations.
Software Supply Chain Vulnerabilities
Automotive software often relies on complex supply chains. Cyber attackers may target vulnerabilities within the supply chain to inject malicious code into the software, posing serious threats to the entire fleet.
Insufficient Encryption
Inadequate encryption protocols can expose communication channels within vehicles, allowing cybercriminals to intercept and manipulate data, compromising both safety and privacy..
Detection and Response Strategies
Detection and response strategies enable real-time monitoring, rapid identification, and immediate response to potential threats, safeguarding critical components from unauthorized access or manipulation.
Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS)
Implementing robust IDS helps in real-time monitoring of network traffic and system activities. Unusual patterns or suspicious activities can be quickly identified, allowing for immediate response.
Continuous Security Audits
Regular security audits of auto software can uncover potential vulnerabilities. These audits should encompass the entire software supply chain to ensure that every component is secure and up to date.
Enhanced Authentication Mechanisms
Strengthening authentication protocols, including multi-factor authentication, helps prevent unauthorized access and manipulation of critical software components, especially in the context of electric vehicle batteries.
Secure Over-the-Air (OTA) Updates
Establishing a secure and reliable method for delivering software updates is crucial. Implementing secure OTA updates ensures that the software can be patched promptly to address newly discovered vulnerabilities. This ensures that any issues can be promptly fixed.
Safeguarding the Future of Automotive Software Security
As the automotive industry continues to evolve, the importance of cybersecurity in auto software cannot be overstated and must be taken seriously by everyone in the industry. Collaborative efforts between automakers, software developers, and cybersecurity experts are essential to stay ahead of emerging threats. Industrywide standards and regulations must be established and adhered to, fostering a proactive approach to cybersecurity rather than a reactive one.
The marriage of automotive software and cybersecurity is an imperative aspect of ensuring the safety and reliability of modern vehicles, particularly with the advent of electric vehicles. By understanding and addressing vulnerabilities through effective detection and response strategies, the automotive industry can safeguard its future and reinforce the commitment to fleet safety in the ever-evolving landscape of connected and digitally-driven automobiles.









More Stories
Auto Repair Services: Keeping Your Vehicle Road-Ready
Unleashing Creativity with Vidnoz: The Best Free AI Video Generator in 2025
The Connection Between Air Drying and Energy Efficiency in Industrial Settings